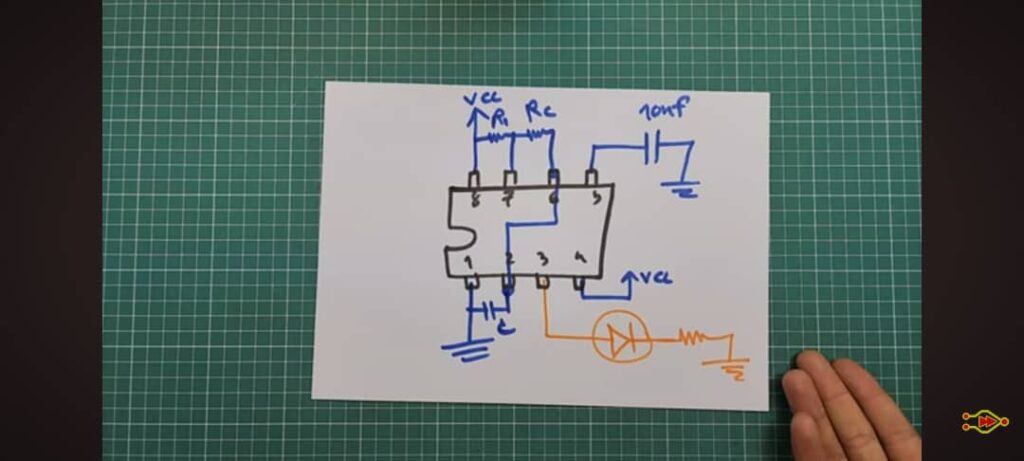
The NE555 Timer IC is one of the most popular and versatile integrated circuits in electronics. It operates in three distinct modes—astable, bistable, and monostable—making it perfect for building simple yet powerful timer-based circuits. In this article, we will explore three basic yet exciting projects using the NE555: Astable Mode – Free-Running Oscillator Using the NE555 Timer Purpose:To make an LED blink continuously (turning ON and OFF repeatedly) without the need for any button press. Components Required:NE555 Timer IC3 × Resistors (e.g., 2.2 kΩ each)2 × Capacitors (e.g., 10 µF )LEDPower source (e.g., 9 V battery) Working Principle:1. No button is needed; the 555 automatically triggers itself.2. Capacitor charges and discharges between 1/3 and 2/3 of supply voltage through the two resistors.3. This produces a continuous HIGH and LOW output on pin 3, which causes the LED to blink repeatedly. Pin Connections: PIN FUNCTION CONNECTION 1 GND Battery -ve 8 VCC Battery +ve 3 Output Connected to LED through 1kΩ resistor 2 Trigger Connected to pin 6 (threshold) and also a capacitor 6 Threshold Connected to pin 2 (trigger) and a resistor 4 Reset Tied to VCC (disables auto-reset) 5 Control Voltage Connected to 10nF capacitor to GND 7 Discharge Connected between two resistors (R1 and R2) Operation:• The NE555 timer continuously switches between HIGH and LOW output states:• No buttons are needed — the circuit self-triggers automatically.• The capacitor charges and discharges through R1 and R2, causing:• Pin 3 Output HIGH: LED turns ON• Pin 3 Output LOW: LED turns OFF• This cycle repeats, making the LED blink continuously without manual input. This setup transforms the 555 timer into a free-running oscillator, ideal for timing, blinking, or pulse-generating applications. Img i. A Schematic Diagram of the Astable Mode 2. Bistable Mode – Flip-Flop Using NE555 Purpose:To create a circuit that stays ON or OFF until a button is pressed — perfect for making toggle switches or memory elements. Components Required:NE555 Timer IC2 Push Buttons (Red = Set, Black = Reset)LED3 ResistorsCapacitor (103 = 10nF)9V Battery Working Principle:The bistable mode has two stable states• ON: LED remains ON after pressing the SET button• OFF: LED remains OFF after pressing the RESET buttonThis behavior mimics a flip-flop, where the state only changes when an external input (button press) occurs. Pin Connections: PIN FUNCTION CONNECTION 1 GND Battery -ve 8 VCC Battery +ve 3 Output Connected to LED 2 Trigger Connected to SET button (Red) 6 Threshold Connected to RESET button (Black) 4 Reset Tied to VCC (disables auto-reset) 5 Control Voltage Connected to 10nF capacitor to GND 7 Discharge Not used Operation:• Pressing SET (Red): Sends LOW to Pin 2 → Output goes HIGH → LED turns ON• Pressing RESET (Black): Sends LOW to Pin 6 → Output goes LOW → LED turns OFFThis simple behavior demonstrates how a 555 timer can function as a manual switch with memory 3. Monostable Mode – One-Shot Timer Using NE555 Purpose:To turn ON an LED for a brief, specific duration when a button is pressed — commonly used in buzzers, timers, and alarms. Components Used:• NE555 Timer IC• Push Button• Capacitor (10µF)• Resistor (10kΩ = 103)• LED• 9V Battery Working Principle:The monostable mode has one stable state (OFF). When triggered, the output goes HIGH temporarily, then returns to LOW automatically.1. Idle: Output is LOW (LED OFF)2. Button Pressed: LOW on Pin 2 triggers the timer → Output goes HIGH (LED ON)3. After Delay: Capacitor charges → Output returns to LOW (LED OFF) Time Delay Formula:T ≈ 1.1 × R × CWhere:T is the time delay in secondsR is the resistance in ohms (Ω)C is the capacitance in farads (F) Example:If R = 10 kΩ and C = 10 µF: T ≈ 1.1 × 10,000 × 0.00001 = 0.11 seconds Pin Connections: PIN FUNCTION CONNECTION 1 GND Battery -ve 2 Trigger Push button → GND 3 Output Connected to LED (with current-limiting resistor) 4 Reset Tied to VCC (to prevent unwanted resets) 5 Control Voltage Optional capacitor (10nF) to GND 6 Threshold Connected to Pin 7 7 Discharge Connected to capacitor and resistor 8 VCC Battery +ve Conclusion:These three simple NE555 circuits show how versatile the timer IC can be:Bistable Mode is perfect for toggle switches and memory circuits. Monostable Mode is ideal for timed outputs and one-shot activations. Astable Mode is best for generating continuous pulses, such as blinking LEDs, clock signals, and tone generation. These are beginner-friendly projects to learn about timing, switching, and digital logic using a single IC — making them great for workshops, exhibitions, or practical classroom demos.